Explain HARDWARE & SOFTWARE
Computer Hardware Basics
Hardware – any physical device or equipment used in or with a computer system (anything you can see and touch).
External hardware
- External hardware devices (peripherals) – any hardware device that is located outside the computer.
- Input device – a piece of hardware device which is used to enter information to a computer for processing.
- Examples: keyboard, mouse, trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, joystick, microphone, light pen, webcam, speech input, etc.


- Output device – a piece of hardware device that receives information from a computer.
- Examples: monitor, printer, scanner, speaker, display screen (tablet, smartphone …), projector, head phone, etc.



Internal hardware
- Internal hardware devices (or internal hardware components) – any piece of hardware device that is located inside the computer.
- Examples: CPU, hard disk drive, ROM, RAM, etc.
Computer Software Basics
Computer software
- Software – a set of instructions or programs that tells a computer what to do or how to perform a specific task (computer software runs on hardware).
- Main types of software – systems software and application software.
Application software

- Application software – a computer program that provides users with tools to accomplish a specific task.
- Examples of application software: word processing, spreadsheets, presentation, database management, Internet browsers, email programs, media players, accounting, pronunciation, translation, desktop publishing, enterprise, etc.
System Software
System software – it is designed to run a computer’s hardware and application software, and make the computer system available for use. It serves as the interface between hardware, application software, and the user.
Explain MOUSE & KEYBOARD
Mouse and keyboard fundamentals
The Mouse
A mouse is a peripheral device that you can use to provide input in your desktop computer or laptop. Even though laptops come with a built in touchpad, having a mouse can be helpful and easier to use if you’re going to spend long periods of time on the computer or for activities that require a bit more precision, such as graphic design.


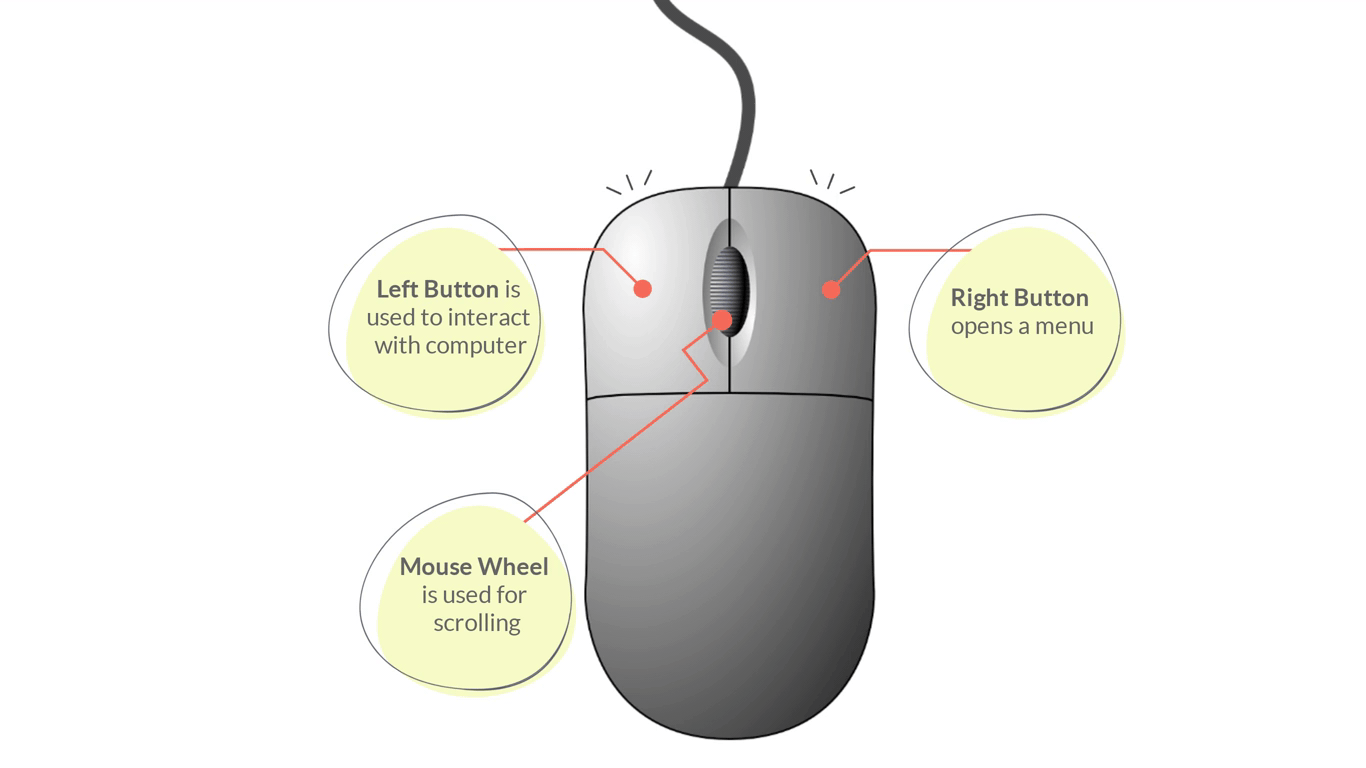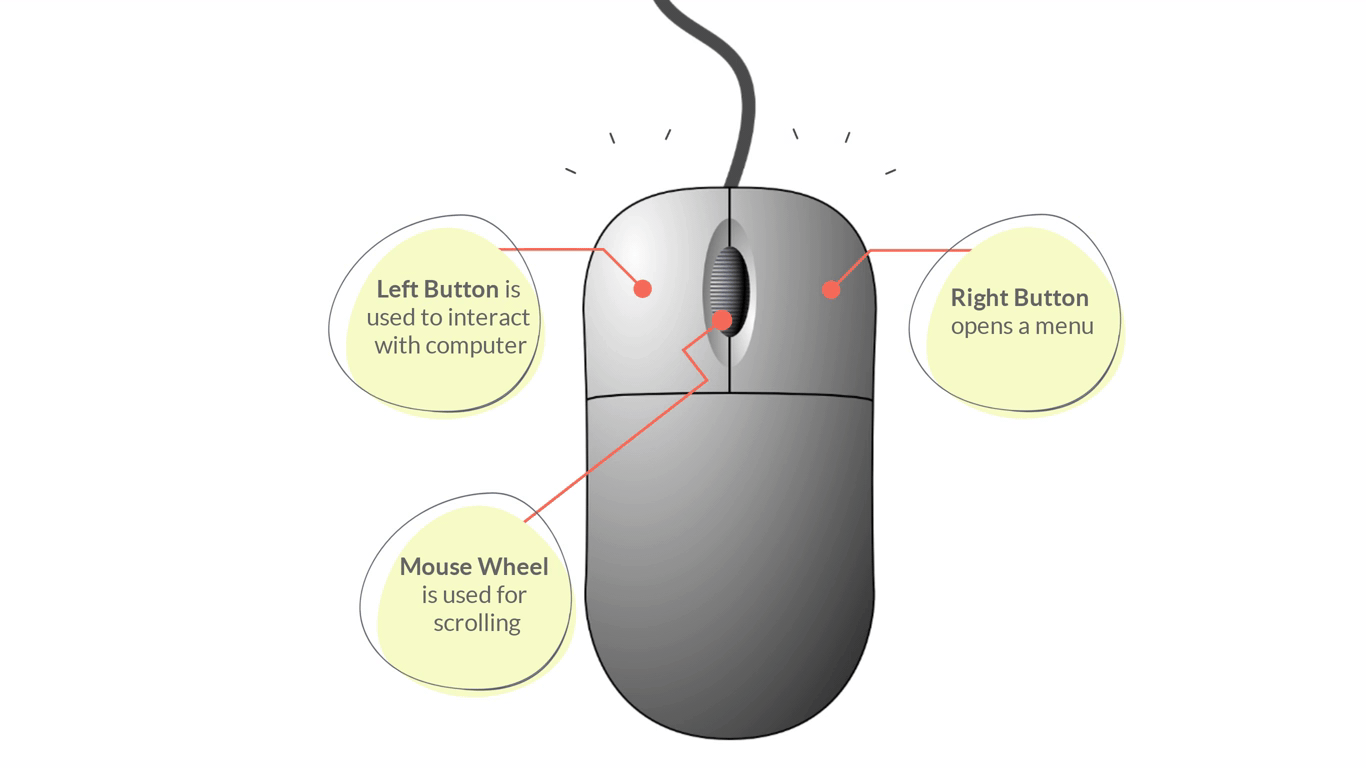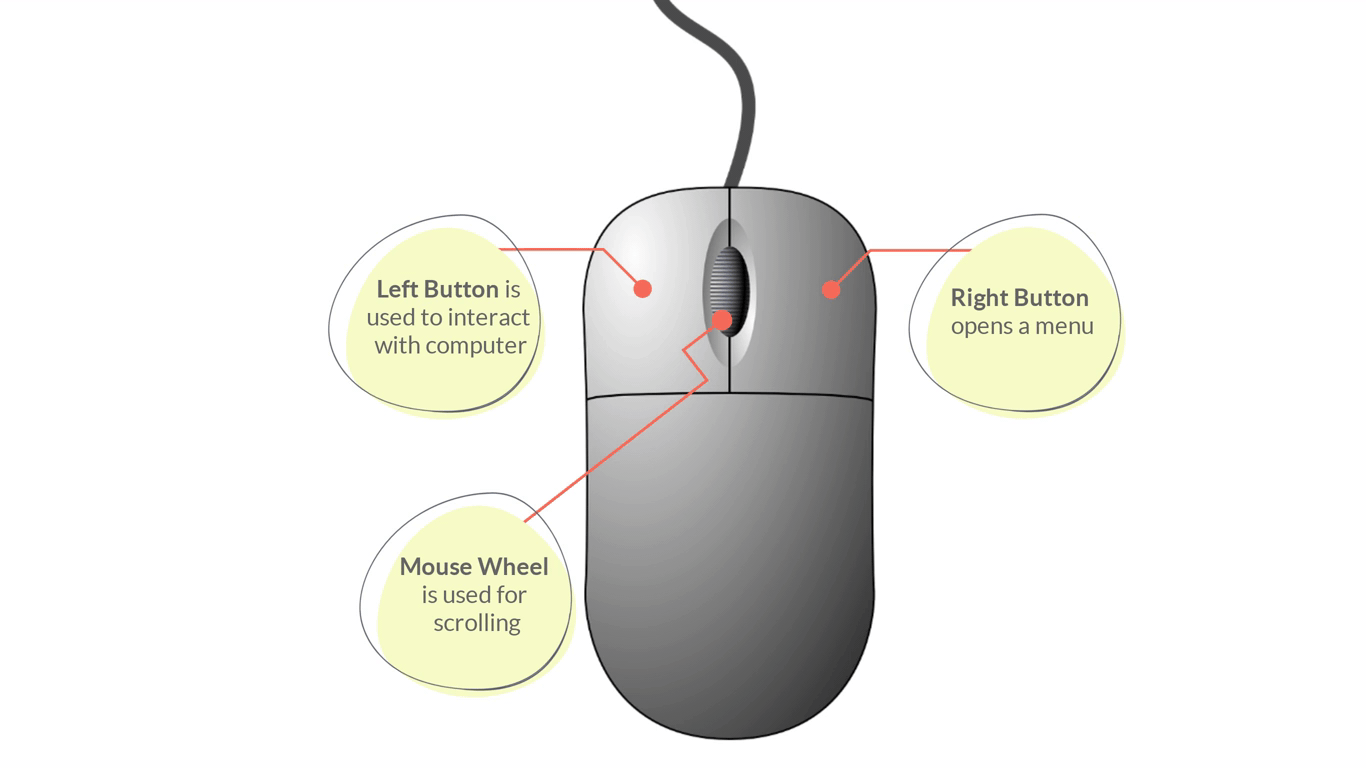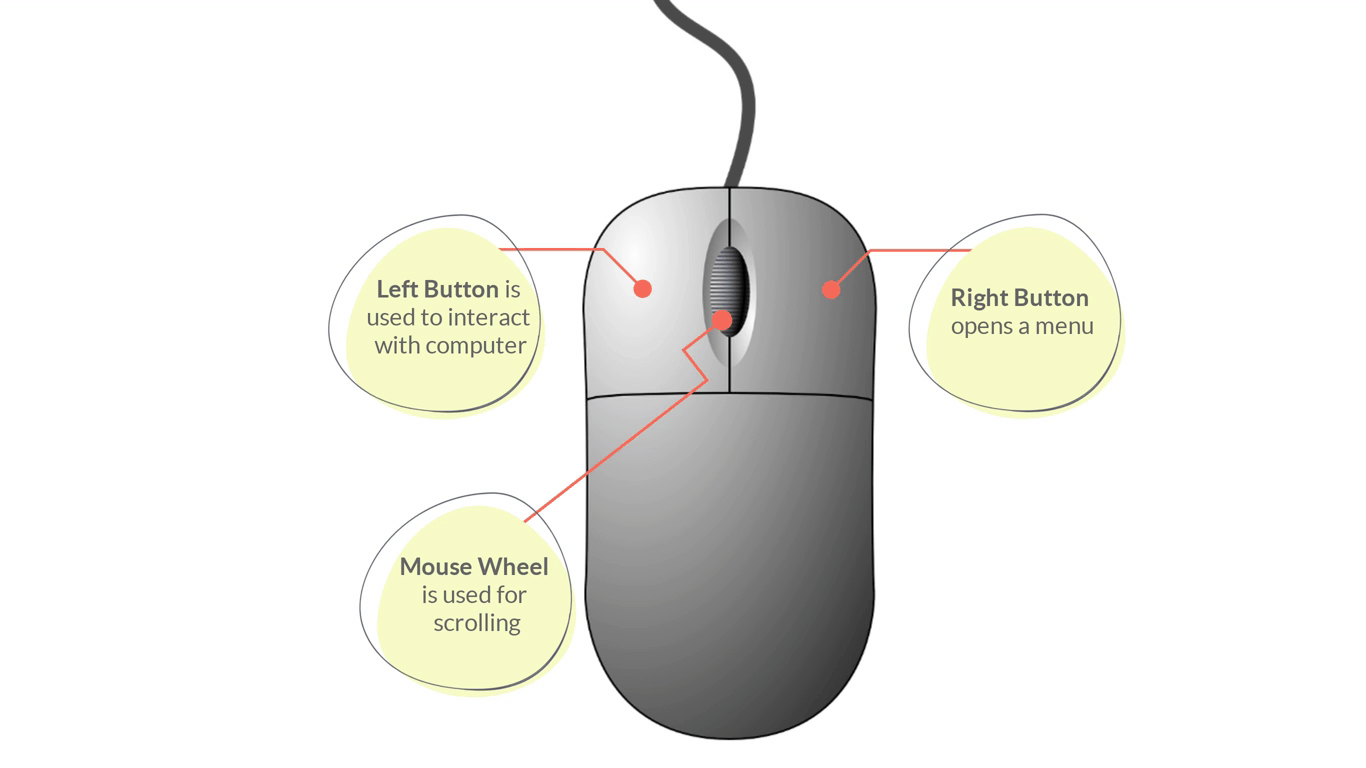
Parts of a Mouse:
- Left/Primary Button – is used most of the time, when interacting with the computer to make a selection.
- Right/Secondary Button – is used less often. When you click the Right button, you can usually access a menu that pops up with several options.
- Mouse Wheel - can be used for scrolling through documents or web pages. However, not all mice have this component.
Mouse operations: Point, Click, Double click, Drag
Placing your mouse on a mouse pad can make it easier to move. As you move your mouse around, you will notice an arrow on the screen moving in the same direction. This arrow is called the mouse pointer and it may appear differently from time to time.
- Pointer pic - Used as a guide for pointing at objects on the computer’s screen.
- Cursor pic - Appearance when editing text documents
- Clickable or Link pic (hand) - Indicates that an item is clickable e.g. button or hyperlink
Mouse pointers can also be customised to take on different appearances.
The Keyboard
The infographic below shows a typical keyboard with its labelled parts e.g. Esc, Function keys, arrow keys, space bar, numeric keys
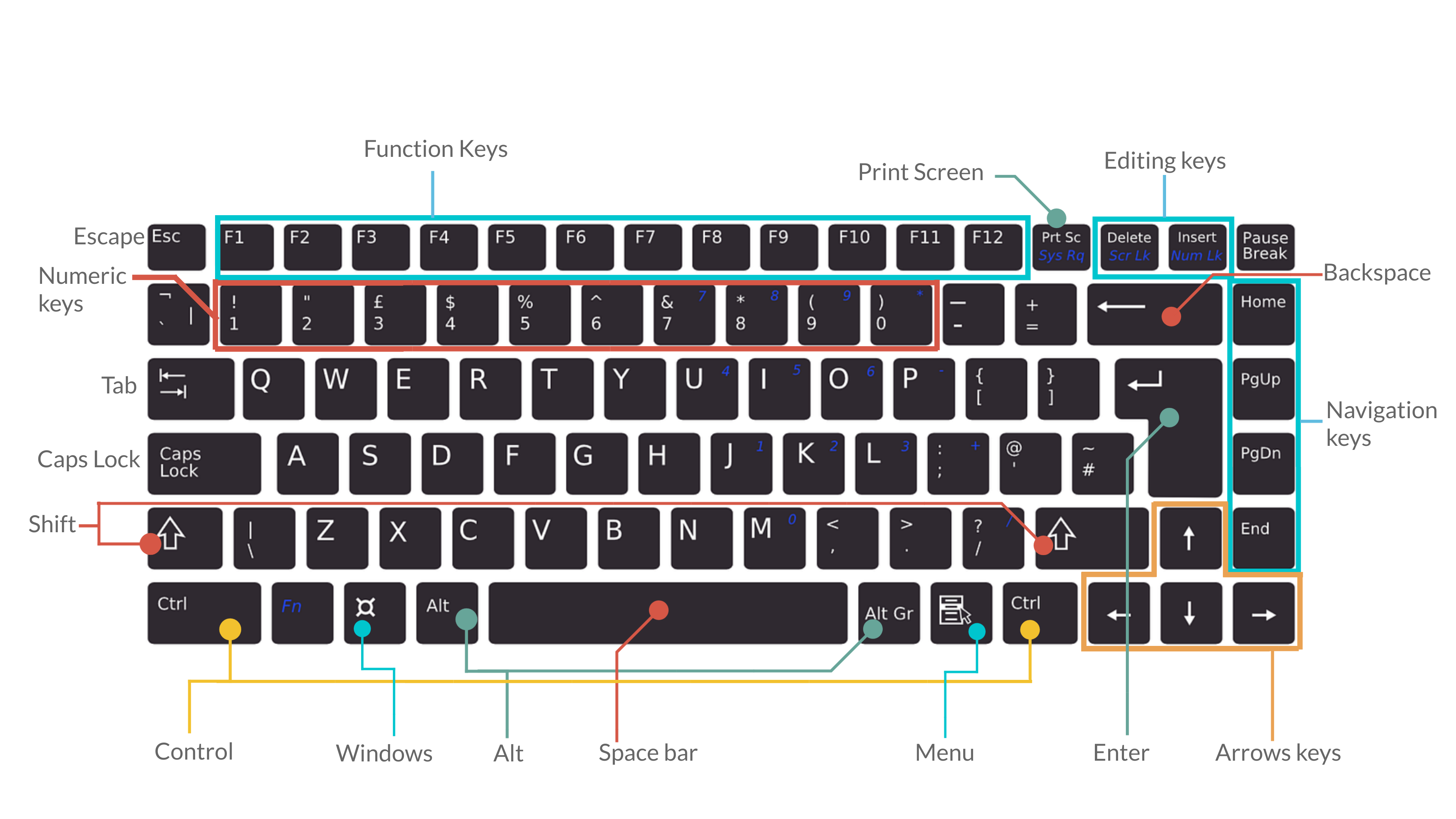
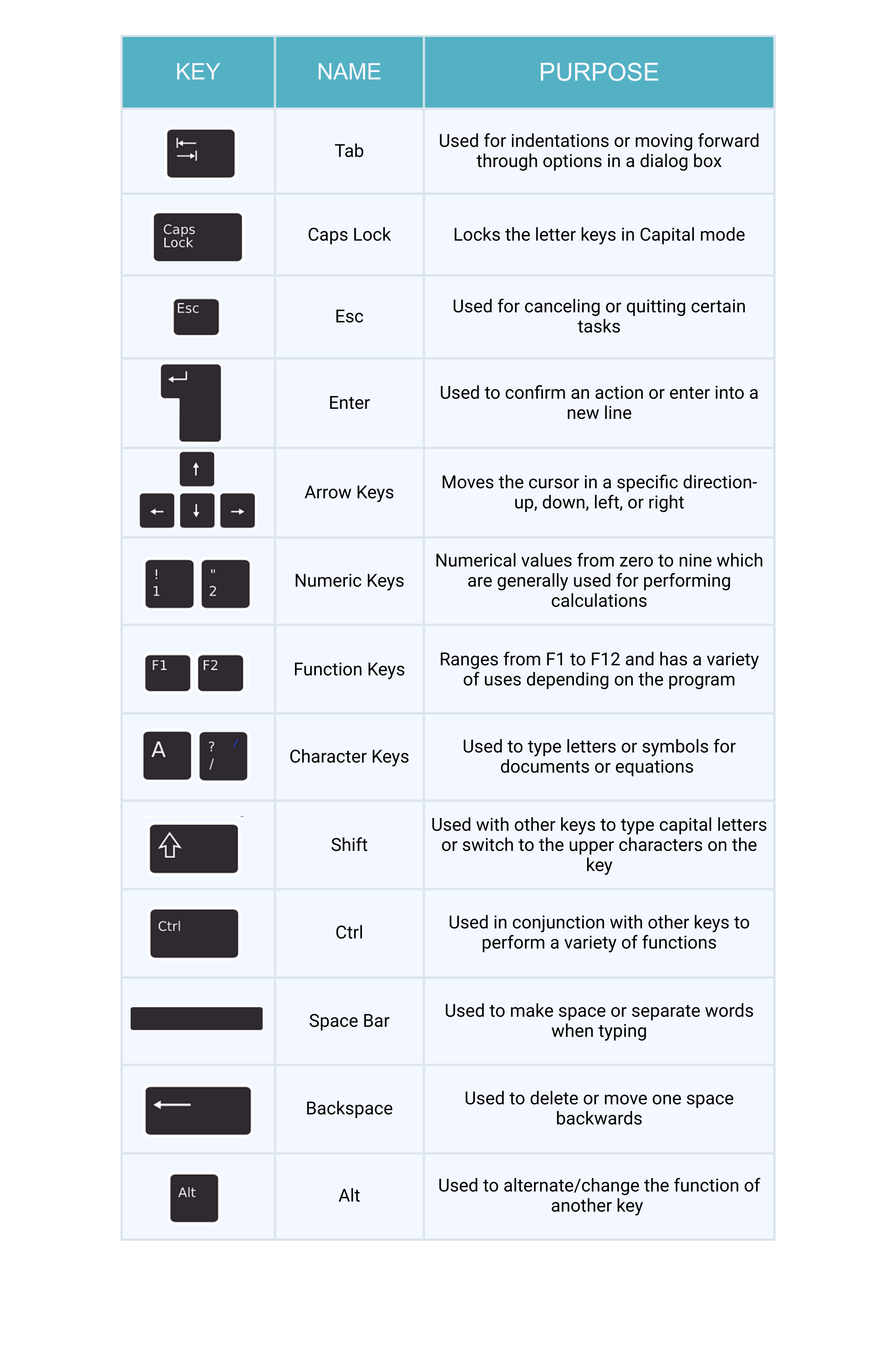
- Tab - For indenting words in a document or for moving forward through options in a dialog box.
- CapsLock - Locks the keyboard in capitals mode, allowing you to type in capital letters.
- Esc - For cancelling or quitting certain tasks in some programs.
- Enter - Also known as the “Hard Return”, the Enter key is used for creating a new line in a document or for selecting/pressing a dialog box button.
- Function keys - These have a variety of uses depending upon the program e.g. F1 offers help in many application programs.
- Arrow keys - To move your cursor and move in specific directions: up, down, left or right.
- Numeric keys - Most of these keys can be used for performing calculations. Some repeat themselves on the keyboard e.g. the number keys are found below the Function keys as well.
DEFINATION OF HTML :-
HTML:- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a text-based approach to describing how content contained within an HTML file is structured. This markup tells a web browser how to display text, images and other forms of multimedia on a webpage.
HTML is a formal recommendation by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and is generally adhered to by all major web browsers, including both desktop and mobile web browsers. HTML5 is the latest version of the specification.
Basic elements of HTML
Using HTML, a text file is further marked up with additional text describing how the document should be displayed. To keep the markup separate from the actual content of the HTML file, there is a special, distinguishing HTML syntax that is used. These special components are known as HTML tags. The tags can contain name-value pairs known as attributes, and a piece of content that is enclosed within a tag is referred to as an HTML element.
HTML elements always have opening tags, content in the middle and closing tags. Attributes can provide additional information about the element and are included in the opening tag. Elements can be described in one of two ways:
- Block-level elements start on a new line in the document and take up their own space. Examples of these elements include headings and paragraph tags.
- Inline elements do not start on a new line in the document and only take up necessary space. These elements usually format the contents of block-level elements. Examples of inline elements include hyperlinks and text format tags.
Commonly used HTML tags
HTML tags dictate the overall structure of a page and how the elements within them will be displayed in the browser. Commonly used HTML tags include:
- <h1> which describes a top-level heading.
- <h2> which describes a second-level heading.
- <p> which describes a paragraph.
- <table> which describes tabular data.
- <ol> which describes an ordered list of information.
- <ul> which describes an unordered list of information.
thanks for visite to this Website guys✌👇👇😉👐 ....................
👇👇🙏🙏 please support to my social media accounts


No comments:
Post a Comment