What is computer virus?
A computer virus is a type of malware that attaches to another program (like a document), which can replicate and spread after a person first runs it on their system. For instance, you could receive an email with a malicious attachment, open the file unknowingly, and then the computer virus runs on your computer. Viruses are harmful and can destroy data, slow down system resources, and log keystrokes.
Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS
Many computer viruses target systems running Microsoft Windows. Macs, on the other hand, have enjoyed a reputation as virus-proof super machines, but in Apple’s own admission, Macs do get malware. There are more Windows users in the world than Mac users and cybercriminals simply choose to write viruses for the operating system (OS) with the largest amount of potential victims.
Today, the “computer” in our pockets may be the one we use most often: our smartphones. Android and iOS are susceptible to various forms of malware, too. Fortunately, most cybersecurity companies like Malwarebytes offer protection for Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS today.
Computer virus examples
Sometimes to understand what something is, we have to examine what it isn’t. Keeping that in mind, let’s play: Is It a Virus?
In the Is It a Virus game we’re going to take a look at examples of things people on the Internet commonly believe to be a virus and explain why it is or isn’t. What fun!
Is a Trojan a virus? Trojans can be viruses. A Trojan is a computer program pretending to be something it’s not for the purposes of sneaking onto your computer and delivering some sort of malware.
History of computer viruses
Today’s malware authors owe a lot to the cybercriminals of yesteryear. All the tactics and techniques employed by cybercriminals creating modern malware were first seen in early viruses. Things like Trojans, ransomware, and polymorphic code. These all came from early computer viruses. To understand the threat landscape of today, we need to peer back through time and look at the viruses of yesteryear.
1984, Computer virus, defined
In 1984 computer scientist Fred Cohen handed in his graduate thesis paper, Computer Viruses – Theory and Experiments in which he coined the term “computer virus,” which is great because “complicated self-reproducing automata” is a real mouthful. In the same paper, Cohen also gave us our first definition of “computer virus” as “a program that can ‘infect’ other programs by modifying them to include a possibly evolved copy of itself.”
1999, “You’ve got mail (and also a virus)”
Think back to 1999. If someone you knew sent you an email that read “Here is the document you requested … don’t show anyone else ;-),” you opened the attachment.
This was how the Melissa virus spread and it played on the public’s naiveté about how viruses worked up to that point. Melissa was a macro virus. Viruses of this type hide within the macro language commonly used in Microsoft Office files. Opening up a viral Word doc, Excel spreadsheet, etc. triggers the virus.
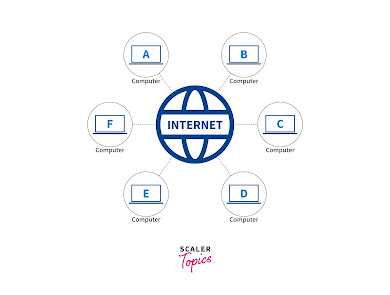
How Does the Internet Work?
What happens when we surf the Internet?
1. Extracting IP address of a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) In our browser, we enter the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) address of the website we want to visit. Once we enter the URL address of the website, the browser with the help of the DNS (Domain Name System) extracts the IP address corresponding to the URL address that is entered. The DNS (Domain Name System) contains the mapping of the URLs along with their corresponding IP addresses.
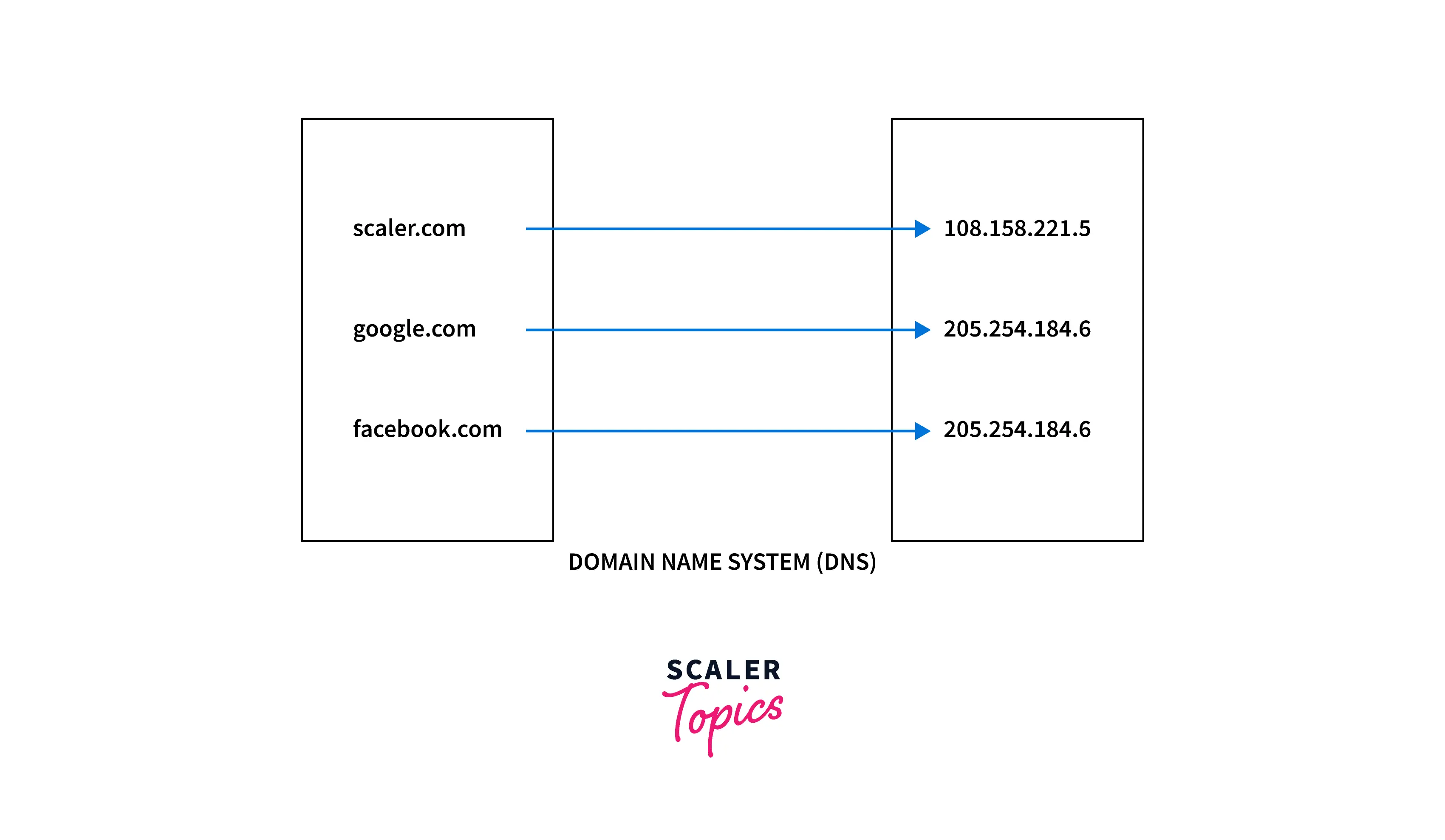
2. Sending request to the server to access the webpage and receiving response Once we get the IP address of the website we want to access using DNS, the browser sends an HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) request to the server to extract the HTM (Hypertext Markup Language)L webpage corresponding to the IP address. This request is sent over PORT 80 using TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). Once the server receives this HTTP request, it responds back with an HTTP response. This HTTP response consists of the information related to the HTML page corresponding to the IP address of the website.
thanks for visite to this Website guys✌👇👇😉👐 ....................
👇👇🙏🙏 please support to my social media accounts