Chapter - 4
Lesson name - Library classes
Ques:-1 What's a wrapper classes ?
Ans:- A Wrapper class is a class whose object wraps or contains primitive data types. When we create an object to a wrapper class, it contains a field and in this field, we can store primitive data types. In other words, we can wrap a primitive value into a wrapper class object.'
Need of Wrapper Classes
- They convert primitive data types into objects. Objects are needed if we wish to modify the arguments passed into a method.
- The classes in java.util package handles only objects and hence wrapper classes help in this case also.
- An object is needed to support synchronization in multithreading.
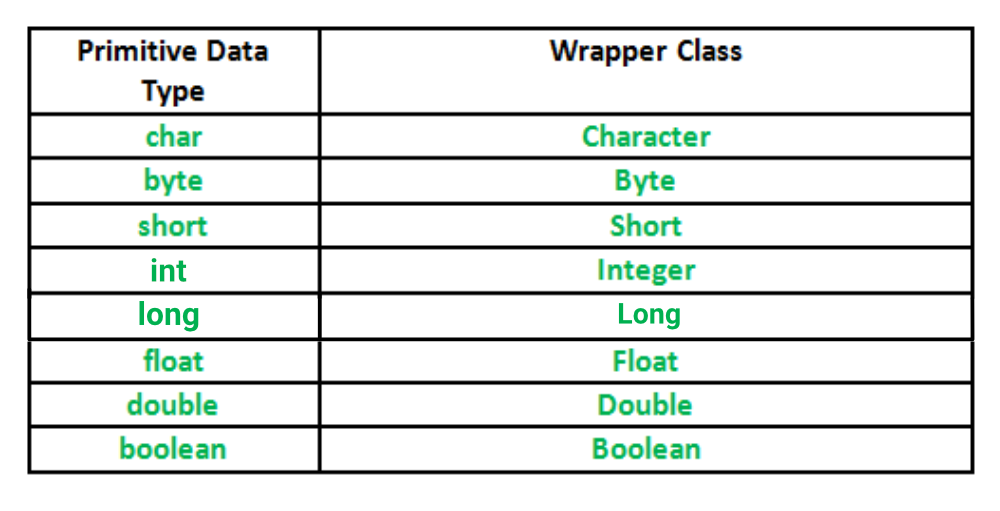
Primitive Data types and their Corresponding Wrapper class
Implementation
Output:
Values of Wrapper objects (printing as objects) Byte object byteobj: 1 Integer object intobj: 10 Float object floatobj: 18.6 Double object doubleobj: 250.5 Character object charobj: a Unwrapped values (printing as data types) byte value, bv: 1 int value, iv: 10 float value, fv: 18.6 double value, dv: 250.5 char value, cv: a
Methods of wrapper classes -
Below table lists wrapper classes in Java API with constructor details.
| Primitive | Wrapper Class | Constructor Argument |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean | boolean or String |
| byte | Byte | byte or String |
| char | Character | char |
| int | Integer | int or String |
| float | Float | float, double or String |
| double | Double | double or String |
| long | Long | long or String |
| short | Short | short or String |
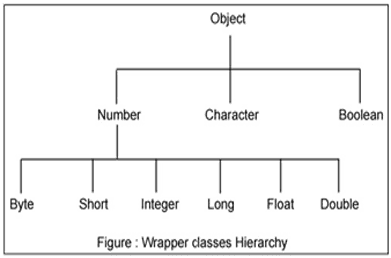
Below is wrapper class hierarchy as per Java API
The most common methods of the Integer wrapper class are summarized in below table. Similar methods for the other wrapper classes are found in the Java API documentation.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| parseInt(s) | returns a signed decimal integer value equivalent to string s |
| toString(i) | returns a new String object representing the integer i |
| byteValue() | returns the value of this Integer as a byte |
| doubleValue() | returns the value of this Integer as a double |
| floatValue() | returns the value of this Integer as a float |
| intValue() | returns the value of this Integer as an int |
| shortValue() | returns the value of this Integer as a short |
| longValue() | returns the value of this Integer as a long |
| int compareTo(int i) | Compares the numerical value of the invoking object with that of i. Returns 0 if the values are equal. Returns a negative value if the invoking object has a lower value. Returns a positive value if the invoking object has a greater value. |
| static int compare(int num1, int num2) | Compares the values of num1 and num2. Returns 0 if the values are equal. Returns a negative value if num1 is less than num2. Returns a positive value if num1 is greater than num2. |
| boolean equals(Object intObj) | Returns true if the invoking Integer object is equivalent to intObj. Otherwise, it returns false. |
This is the same example as your first example