We will learn these ways to create object later.
Objects and Classes in Java
In this page, we will learn about Java objects and classes. In object-oriented programming technique, we design a program using objects and classes.
An object in Java is the physical as well as a logical entity, whereas, a class in Java is a logical entity only.
What is an object in Java

An entity that has state and behavior is known as an object e.g., chair, bike, marker, pen, table, car, etc. It can be physical or logical (tangible and intangible). The example of an intangible object is the banking system.
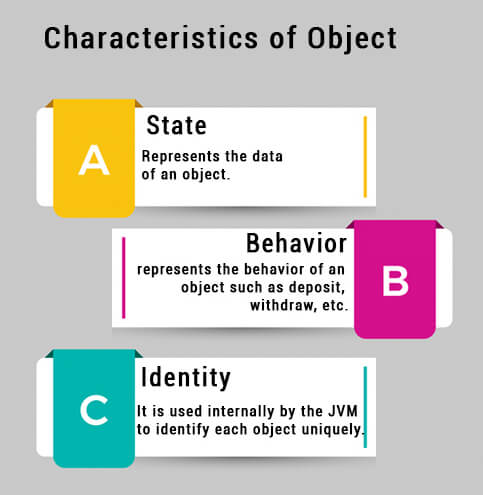
An object has three characteristics:
- State: represents the data (value) of an object.
- Behavior: represents the behavior (functionality) of an object such as deposit, withdraw, etc.
- Identity: An object identity is typically implemented via a unique ID. The value of the ID is not visible to the external user. However, it is used internally by the JVM to identify each object uniquely.
For Example, Pen is an object. Its name is Reynolds; color is white, known as its state. It is used to write, so writing is its behavior.
An object is an instance of a class. A class is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. So, an object is the instance(result) of a class.
Object Definitions:
- An object is a real-world entity.
- An object is a runtime entity.
- The object is an entity which has state and behavior.
- The object is an instance of a class.
What is a class in Java
A class is a group of objects which have common properties. It is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. It is a logical entity. It can't be physical.
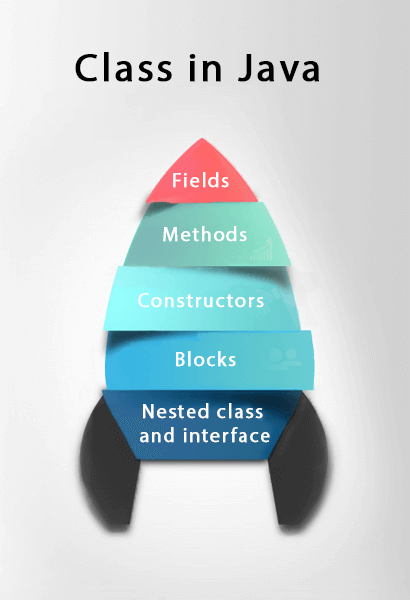
A class in Java can contain:
- Fields
- Methods
- Constructors
- Blocks
- Nested class and interface
Syntax to declare a class:
Instance variable in Java
A variable which is created inside the class but outside the method is known as an instance variable. Instance variable doesn't get memory at compile time. It gets memory at runtime when an object or instance is created. That is why it is known as an instance variable.
Method in Java
In Java, a method is like a function which is used to expose the behavior of an object.
Advantage of Method
- Code Reusability
- Code Optimization
new keyword in Java
The new keyword is used to allocate memory at runtime. All objects get memory in Heap memory area.
Object and Class Example: main within the class
In this example, we have created a Student class which has two data members id and name. We are creating the object of the Student class by new keyword and printing the object's value.
Here, we are creating a main() method inside the class.
File: Student.java
Output:
0 null
Object and Class Example: main outside the class
In real time development, we create classes and use it from another class. It is a better approach than previous one. Let's see a simple example, where we are having main() method in another class.
We can have multiple classes in different Java files or single Java file. If you define multiple classes in a single Java source file, it is a good idea to save the file name with the class name which has main() method.
File: TestStudent1.java
Output:
0 null

No comments:
Post a Comment